Recent jumps in FAANG stocks indicate vulnerabilities for banks
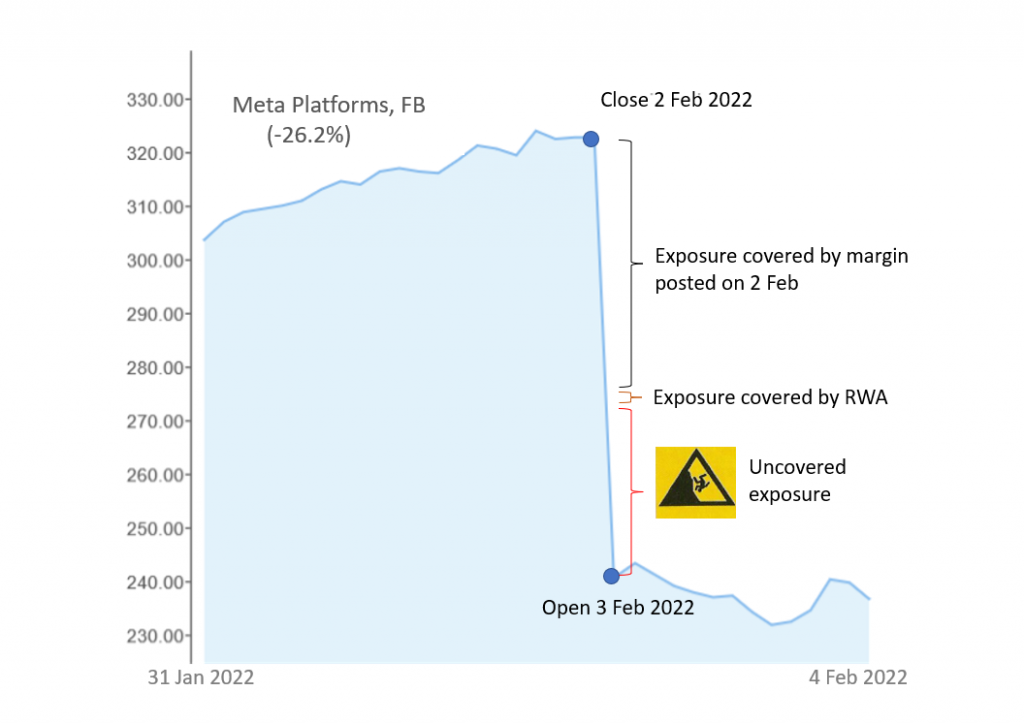
Last week, the shares of US tech giants Amazon and Facebook owner Meta Platforms showed exceptional price swings. Both shares are widely held by hedge funds. According to Reuters, eight hedge funds may have lost more than $5 billion in paper profits on their investments in Meta when the shares dropped 26.4% on Thursday, 3 February 2022.1 Similarly, hedge funds might have lost significant amounts on their short positions when the share price of Amazon rose by 13.5% on Friday, 4 February 2022.
Hedge funds and family offices are often operating with significant leverage. It is not untypical for them to enter their positions through equity swaps. Under such structures, the banks buy the shares on their own account and pass the P&L to their clients via Total Return Swaps (TRS). To ensure the clients are able to meet their payment obligations from the swap transactions, collateral has to be provided to the bank as margin. For so called uncleared swaps, international regulations require the clients to post 15% of an equity swap’s notional amount as initial margin. Subsequent price changes are then settled via variation margin payments on a daily basis.
On 2 February 2022, Meta Platforms missed analysts’ profit expectations and issued a profit warning. In after-hours trading, the stocks dropped sharply and opened at $244.652 the following morning, down 24.3% from the prior day closing price used for the margin calculation. Thus, a material part of the banks’ swap counterparty exposures was temporarily uncovered and likely triggered several margin calls. This was no issue if all clients were able to make the required variation margin payments. Yet, the banks were exposed to increased risk. Given that eight hedge funds held according to Reuters alone exposures of $20bn in Meta by end of 3Q21, it is to be assumed that on 3 February the aggregated variation margin amount due by clients to their banks summed up to billions.
The loss potential revealed by the unusually large price jumps in the two blue chip tech stocks stands in sharp contrast to the only low regulatory capital need for collateralized OTC derivatives. Orbit36 estimates that the aggregated capital requirement for equity swaps on Meta Platforms amounts to only few hundred million dollars, based on an approximated risk weight of around 3.5% under the standardized counterparty credit risk model SA-CCR. The assumptions used for the calibration of this model are not appropriate in the current market environment.
Orbit36 recommends banks and regulators to closely monitor open equity swap positions for potential credit exposures subsequent to large market moves. What happened last week in two special situations could point to a hidden systemic risk. We have the necessary expertise to review your derivative portfolios for vulnerabilities which may remain undetected by commonly used models.
1) Reuters, Facebook-owner Meta was popular stock for hedge funds before the slide, 3 February 2022, Maiya Keidan, available on https://www.reuters.com/technology/clutch-hedge-funds-held-meta-shares-may-have-been-punished-2022-02-03/
